Patient Engagement: 3 digital strategies to increase patient activation and better health outcomes
The concept of patient engagement has become increasingly important in healthcare as the focus shifts towards providing patient-centred care. Patients who are actively engaged in their care tend to have better outcomes, including fewer hospital admissions, better management of chronic conditions, and improved quality of life. By fostering collaboration and shared decision-making between patients and healthcare providers, patient engagement can improve health outcomes and overall patient satisfaction.
Digital strategies have become a key component of patient engagement in modern healthcare. The use of telemedicine, for example, allows patients to connect with their healthcare providers remotely, reducing the need for in-person appointments and improving access to care. mHealth devices, such as wearable technology and smartphone apps, can help patients monitor their health and provide valuable health data to providers, allowing for more personalised and effective care. Digital educational resources can also have a significant impact on patient engagement, empowering patients with knowledge about their conditions and treatment options.
Therefore, with the rise of digital health, it became easier for healthcare providers to come up with patient engagement strategies to truly involve patients in their own care, improving the adherence to treatment and prevention strategies.
The importance of patient engagement for better health outcomes
Patient engagement involves actively involving patients in their healthcare decision-making and treatment plans. It empowers them to be well-informed and active participants in their care, rather than passive recipients of medical services. This is now a vital aspect of contemporary healthcare, as it can result in enhanced health outcomes and increased patient satisfaction.
These are some approaches used in patient engagement strategies to pave the way for better overall individual and population health.
- Two-way communication: patient engagement fosters open two-way communication between patients and healthcare providers, allowing them to easily voice their concerns and preferences. This collaborative approach leads to personalised treatment plans and better understanding and compliance with the care provided.
- Patient-centred and value-based care models: the global strategy also aligns with patient-centred and value-based care models, which prioritise individual patient needs and preferences. By involving patients in their care decisions, healthcare providers can design treatment plans tailored to each patient’s requests and routine, ultimately improving health outcomes and patient satisfaction.
- Shared decision-making: Engaging patients in shared decision-making also empowers them to be active participants in their treatment plans. This involvement leads to better treatment adherence as they feel more invested in their care.
3 strategies for increasing patient engagement
Several strategies can be employed to increase patient engagement, each with its unique benefits. Most of them are directly connected to digital health, which, as mentioned before, has revolutionised the way that healthcare providers can engage with their patients. Here are the three most significant digital approaches to increasing patient engagement.
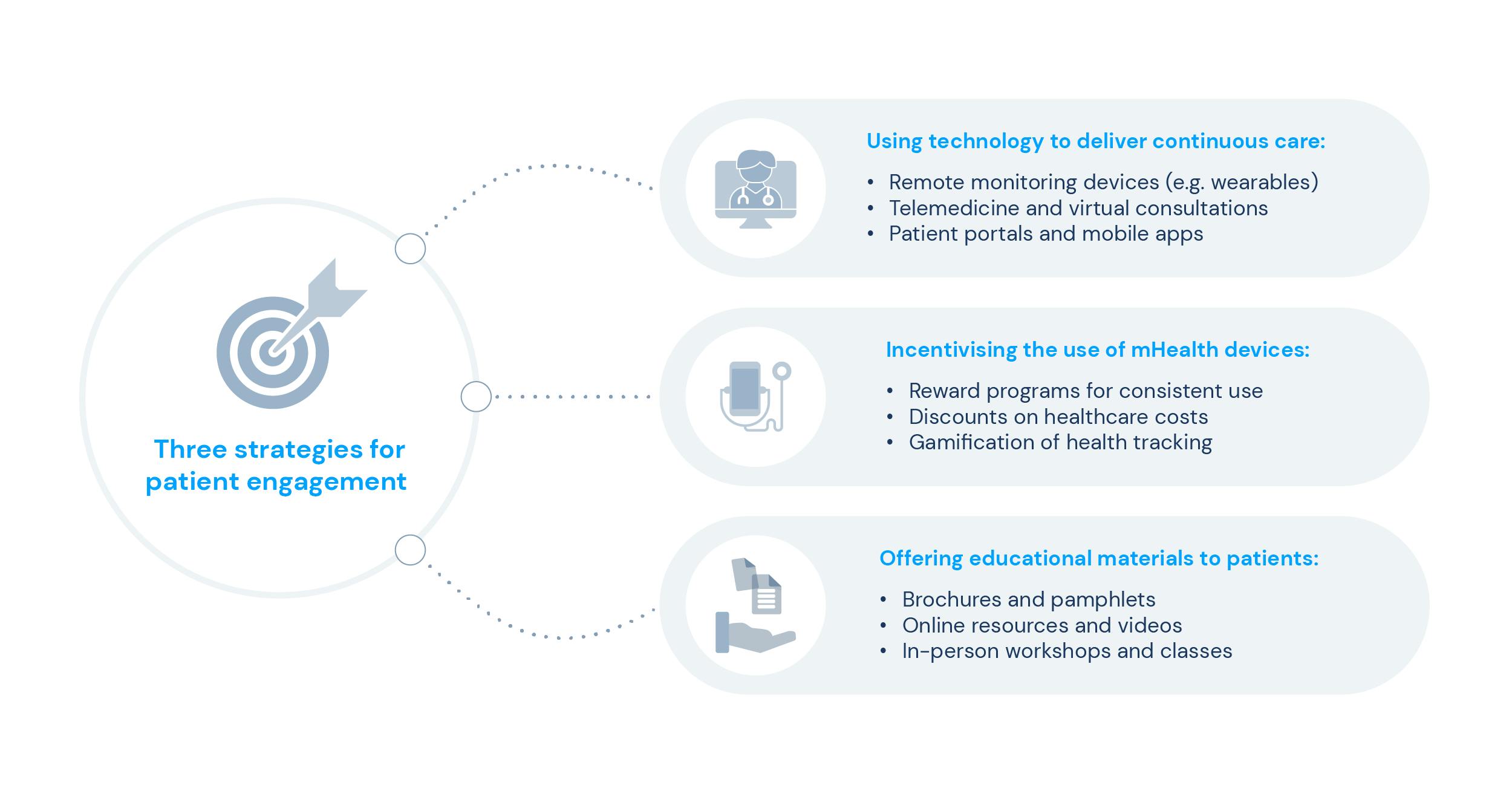
- Usage of technology to deliver continuous care
Technology has revolutionised patient care, enabling continuous monitoring and support outside of traditional clinical settings. Telemedicine has emerged as a popular remote care option, leveraging tools like SMS, automating email communication, and online surveys to connect doctors and healthcare providers with patients in innovative ways. This technology-driven approach offers numerous benefits, including improved access to care for rural and remote populations, enhanced communication leading to better engagement and treatment outcomes, and reduced healthcare costs.
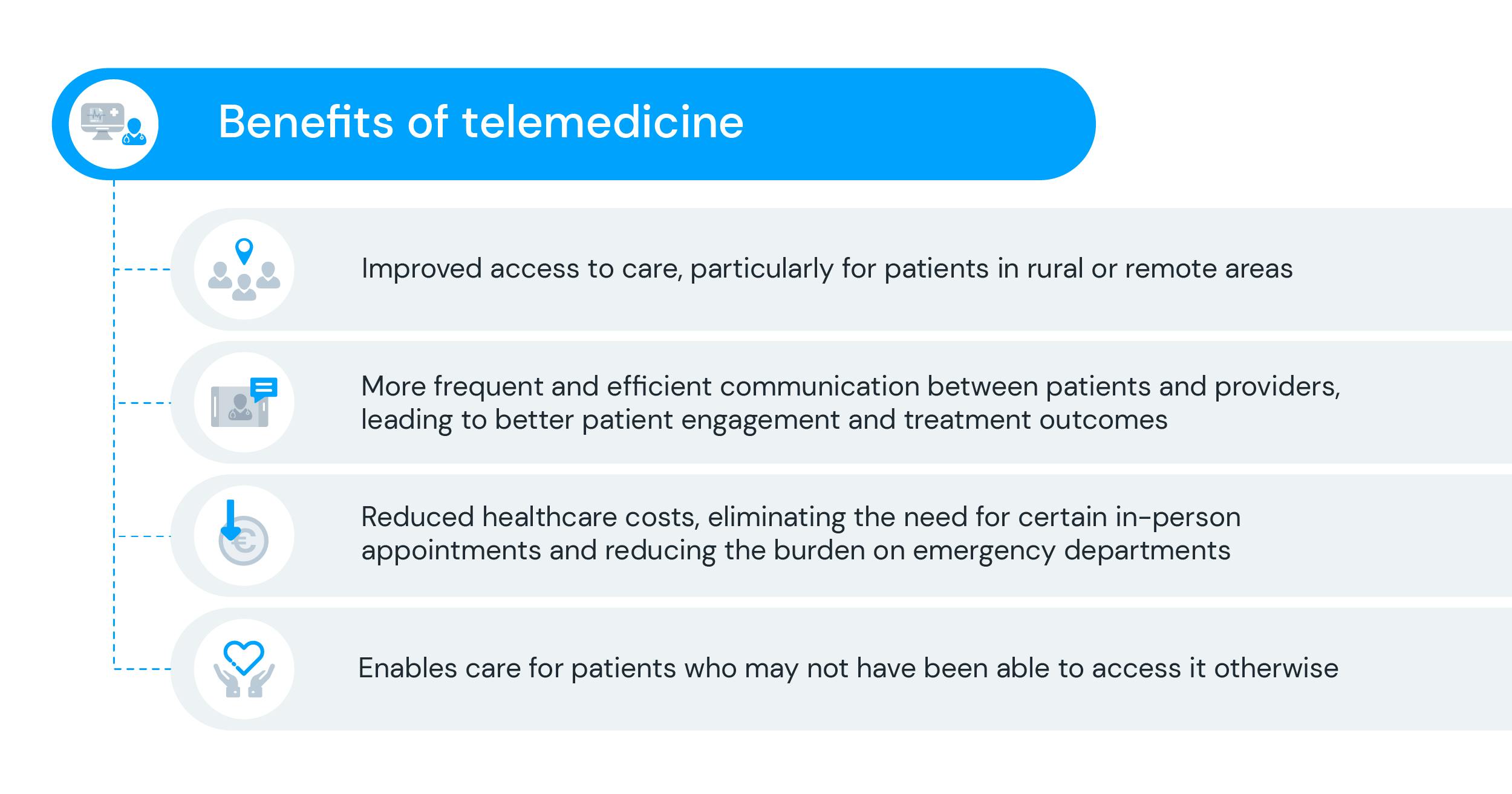
Medical appointments through telemedicine also enable the provision of care to previously underserved patients, regardless of their location. Studies have shown the effectiveness of remote monitoring in the management of chronic diseases, such as obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) and type 2 diabetes, resulting in improved clinical outcomes and quality of life. Thus, the embrace of technology in healthcare is crucial for delivering patient-centred care and ensuring better treatment outcomes as the field continues to evolve.
2. Disseminating the use of mHealth devices
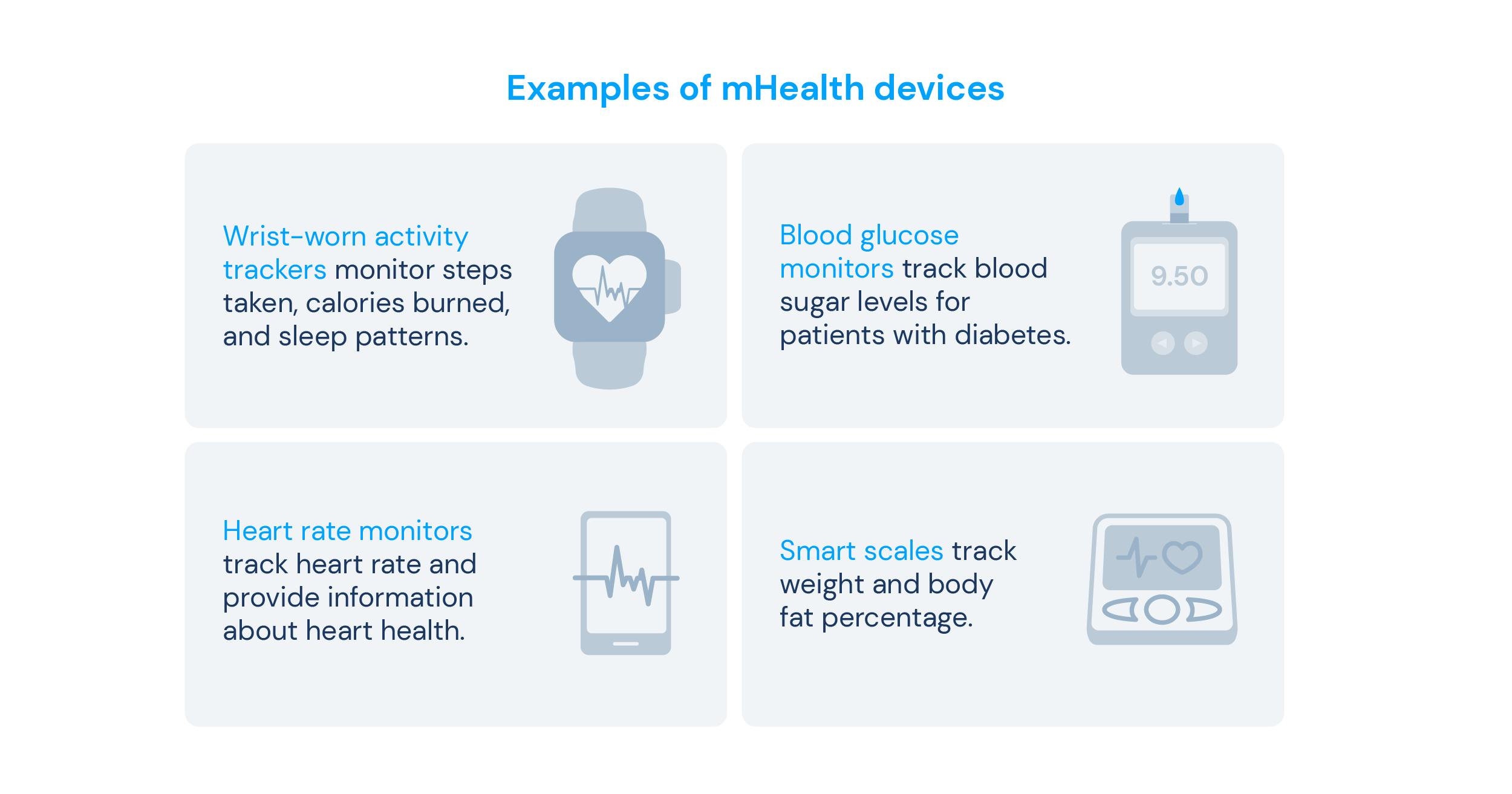
Another digital strategy for patient engagement is using mobile health (mHealth) devices. mHealth is empowering patients to take an active role in their healthcare with devices such as:
- Wrist activity trackers or smartwatches that monitor steps taken, calories burned, and sleep patterns;
- Blood glucose monitors that track blood sugar levels for patients with diabetes4;
- Heart rate monitors that track heart rate variability;
- Smart scales that track weight and body fat percentage.
These devices enable patients to monitor their own health while providing valuable data to healthcare providers. By incentivising the use of mHealth devices, providers can increase patient engagement and develop more personalised treatment plans. The benefits of mHealth devices include empowering patients to proactively manage their health, providing valuable data for effective care, and enabling remote monitoring beyond clinical settings.
The promotion of these devices enhances patient activation, leading to improved health outcomes and better quality of life. Studies have shown positive results in various scenarios, such as increased prenatal visits and reduced mortality rates, as well as improved medication adherence and disease management. Embracing mHealth devices offers an innovative approach to healthcare delivery, ensuring personalised care and remote monitoring for better patient outcomes.
3. Promoting knowledge through educational materials
Providing educational materials to patients is a powerful strategy to enhance patient activation and self-management. By having knowledge about their health conditions, treatments, and risks, they can actively participate in their care and achieve better outcomes.
Educated patients facilitate shared decision-making as they gain a deeper understanding of their health and treatment options, being more likely to collaborate with their healthcare providers and receive patient-centred care, resulting in improved outcomes. Educational materials also emphasise the importance of treatment adherence and the potential consequences of non-compliance. By comprehending the risks, patients are motivated to follow their treatment plans and take the necessary steps to improve their health.
These materials can be delivered in a variety of formats, including brochures, videos, or online resources, through in-person interactions or digital platforms such as patient portals and email.
knok’s take on patient engagement
Patient engagement is essential to patient-centred and value-based care models that prioritise continuity of care and better health outcomes. By fostering two-way communication, patient engagement enables goal alignment and understanding, which are crucial for successful treatments.
By understanding the importance of continuous care technologies, knok has developed a state-of-the-art digital health platform that enables the creation of automated patient journeys tailored to their standards.
Through our platform, healthcare providers and payors are able to create journeys for target groups and map both in-person and digital interactions, such as appointments, lab exams, procedures and others. They can also program automated notifications to be sent by SMS or e-mail to remind patients about a consultation, send clinical surveys and much more.
References
- Wellbox (2021) 5 Essential Patient Engagement Strategies to Drive Better Outcomes.
- Muller Elena (2023). 5 Ways Telehealth Increases Patient Activation. Health recovery solutions.
- Mesquita R, Figueiredo D, Sousa C, Correia C, Costa L, et al. Remote monitoring of patients with COPD: a systematic review. J Med Internet Res. 2018;20(7):e10801. doi: 10.2196/10801
- Sood A, Patel S, Bansal D, Saraf S, Grag R, et al. Home telemedicine for type 2 diabetes: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Telemed Telecare. 2018;24(4):269-82. doi: 10.1177/1357633X17694602
- Lund S, et al. Mobile phones as a health communication tool to improve skilled attendance at delivery in Zanzibar: a cluster-randomised controlled trial. BJOG. 2012;119(10):1256-64.
- Hou C, et al. Mobile phone applications and self-management of diabetes: A systematic review with meta-analysis, study quality grading, and recommendations for future research. J Diabetes. 2018;10(1):28-40.
- Frosch, D. L., et al. "An Effort to Spread Decision Aids in Five California Primary Care Practices Yielded Low Distribution, Highlighting Hurdles." Health Affairs, vol. 31, no. 11, 2012, pp. 2645-2655.
- Tang, T. S., et al. "A Randomized Controlled Trial of a Tailored Interactive Multimedia Computer Program for Improving the Long-term Management of Type 2 Diabetes." Annals of Internal Medicine, vol. 142, no. 11, 2005, pp. 912-919.
- Murray, M. D., et al. "The Impact of Patient Education on Prescription Drug Compliance and Health Outcomes: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis." American Journal of Health-System Pharmacy, vol. 57, no. 4, 2000, pp. 383-396.
- Patient Engagement: Technical Series on Safer Primary Care. Geneva: World Health Organization; 2016. Licence: CC BY-NC-SA 3.0 IGO
- Wellbox (2021) 5 Essential Patient Engagement Strategies to Drive Better Outcomes.
- ArborAdmin (2020) How to Engage Patients and Collect Valuable Patient-Reported Data. Arbor Metrix